A robust RSI trading strategy forex starts with understanding the Relative Strength Index as a momentum tool, then applying it within the broader context of trend, structure, and risk controls. This guide consolidates the essential RSI concepts—settings, overbought/oversold behavior, centerline logic, divergence, and advanced swing rejection—into a practical framework you can validate through historical chart review and execute with clear, rule-based trade management. Throughout, remember: RSI is a momentum indicator. It should not be used in isolation, particularly in strong trends where “overbought” or “oversold” can persist. Confirmation and risk management are non-negotiable.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and magnitude of recent price changes on a bounded scale from 0 to 100. It helps traders gauge when momentum is accelerating or weakening, which can precede pullbacks, reversals, or trend continuations. Unlike a trend indicator, RSI does not tell you the prevailing direction by itself; instead, it shows how forceful the latest price moves have been relative to recent losses or gains.
Traders use RSI to:
Because RSI is a momentum indicator, it is most effective when combined with trend assessment and key levels. Overbought/Oversold readings alone are unreliable within strong trends.
RSI uses average gains and losses over a chosen period (commonly 14) and normalizes them to a 0–100 scale. The core expression is:
RSI = 100 - [100 / (1 + RS)]
where RS is the ratio of average gains to average losses over the lookback.
Key steps:
The formula matters because it keeps RSI bounded, making 30/70 thresholds and the 50 centerline meaningful reference points for momentum behavior.
The 14-period input—popularized by J. Welles Wilder—balances responsiveness and noise. In the RSI 14 strategy forex, the standard 14 setting is widely used because it captures a representative sample of recent momentum without whipsawing excessively. For most currency pairs and conditions, 14 provides a stable baseline for trend confirmation via the 50 line and for interpreting overbought/oversold zones.
Considerations for RSI settings forex:
Regardless of the period, always prioritize confluence: align RSI insights with trend direction, market structure, and risk management.
The classic rsi overbought oversold forex approach uses the 70/30 thresholds to frame potential exhaustion. However, 70 or 30 are not “press buy/sell” signals; they are warnings that momentum is stretched. In a strong uptrend, price can hold above 70 for extended periods, and in a strong downtrend, below 30 for longer than expected. This is why the RSI 30/70 strategy must include confirmation:
Practical rules:
Risk management:
The RSI 50 level acts as a directional filter. While not a trend indicator by itself, RSI crossing and holding above 50 typically reflects net positive momentum; crossing and holding below 50 reflects net negative momentum. Traders use it to:
This centerline logic reduces whipsaws associated with trading extremes blindly, particularly during strong trends—where the “overbought” or “oversold” labels can remain for a long time.
Divergence is the disagreement between price and momentum. If price makes a new extreme but RSI does not confirm, it warns that trend strength may be waning (regular divergence). Hidden divergence, by contrast, often signals continuation after a pullback. Divergence is best traded with confirmation—such as a manual break of minor structure, an RSI centerline crossover, or a clear reversal candle at a key level—because divergence alone can persist for multiple swings, especially in strong trends.
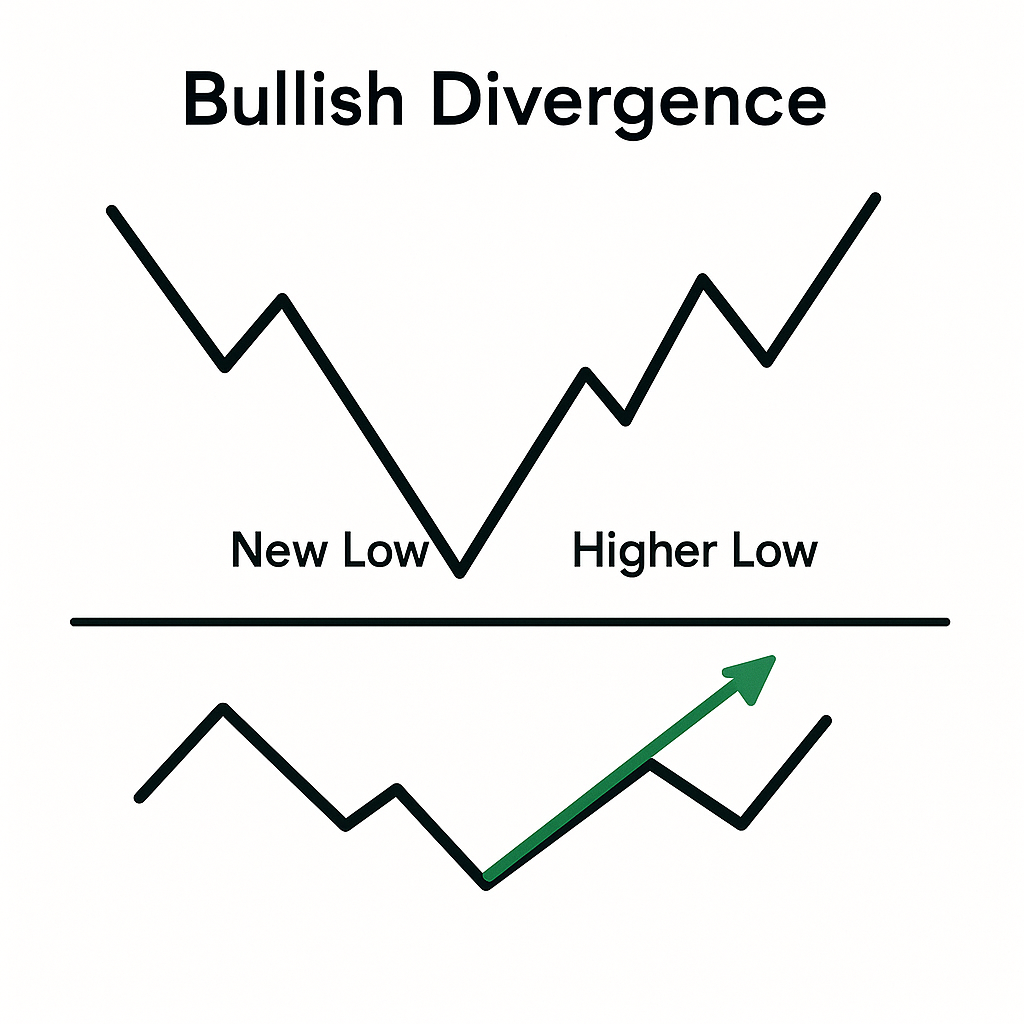
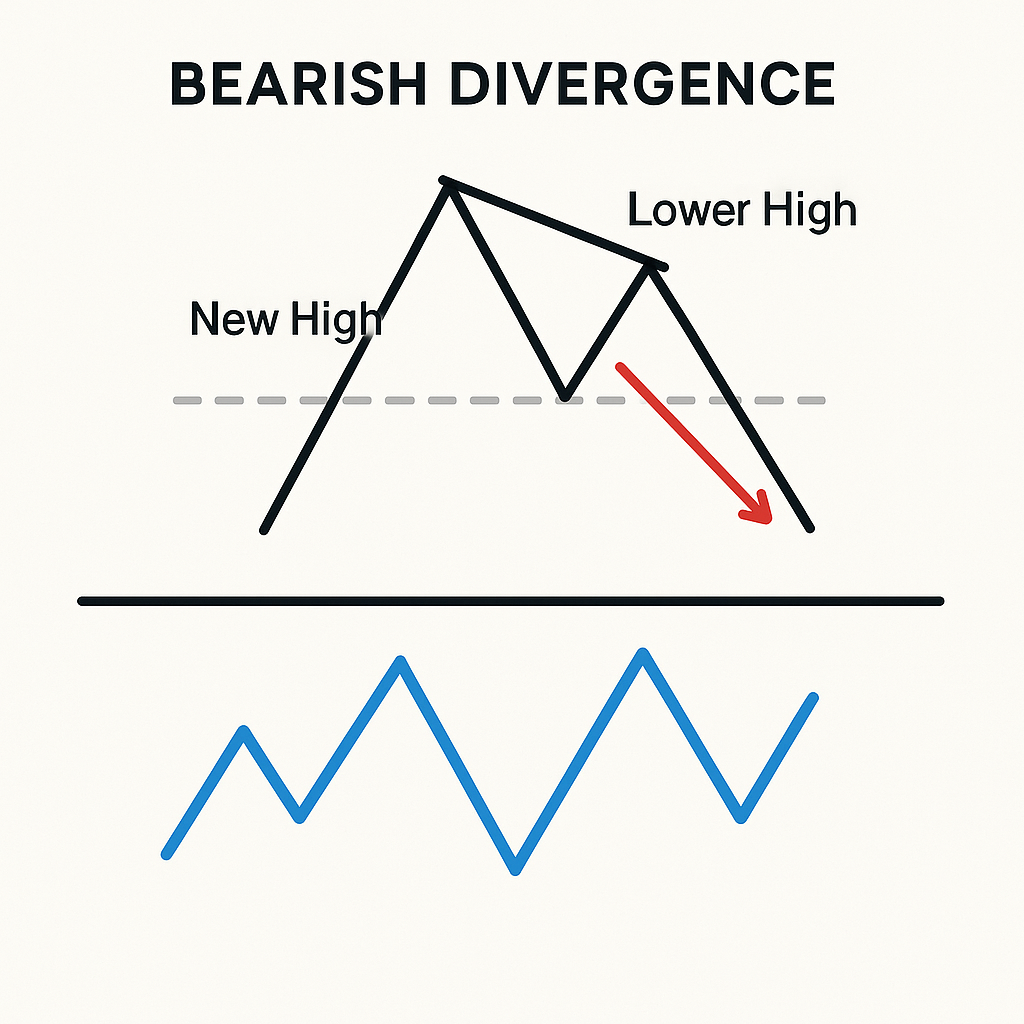
Regular divergence (potential reversal):
Hidden divergence (potential trend continuation):
Execution guidelines:
Swing rejection isolates momentum failure at an extreme and often anticipates a pivot. A common bullish variant:
This sequence reflects sellers losing control before price fully reveals it. The bearish version mirrors the steps at 70:
Tactics:
RSI gains strength when used for momentum confirmation alongside trend or structure tools. The aim is alignment: trade directionally when multiple tools say the same thing, and de-emphasize pure threshold readings in isolation.
The RSI + MACD strategy forex blends momentum (RSI) with trend and momentum histogram dynamics (MACD). A practical framework:
This combination helps avoid the common pitfall of shorting “overbought” RSI during a strong MACD-uptrend or buying “oversold” RSI in a MACD-downtrend.
RSI is well-suited to validating structure:
Rules of thumb:
Timeframe changes alter volatility and signal density. Short timeframes require tighter controls and often shorter RSI periods; longer timeframes benefit from standard or longer periods, with more time to confirm signals and manage trades. Regardless of timeframe, risk per trade and overall risk exposure must stay consistent with a tested plan.
Scalpers and intraday traders often prefer higher sensitivity, using RSI settings around 5–9 and emphasizing the 50-level filter with session levels. In RSI scalping forex, the goal is to align quick momentum turns with micro-structure (e.g., minor swing breaks) while avoiding countertrend fades in strong moves. Consider anchoring bias with a higher timeframe (e.g., M15/H1), then executing on M1–M5 with a faster RSI.
| RSI Period | Timeframe Focus | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | M1–M5 | Very responsive; early momentum cues | High noise; more false signals; requires strict filters |
| 7 | M1–M15 | Balanced sensitivity for scalping/day trades | Still choppy in fast markets; needs confluence |
| 9 | M5–M15 | Smoother than 7; fewer whipsaws | Slightly later signals; can miss rapid flips |
| 14 | M5–H1 | Stable baseline; reliable 50-level reads | Slower for pure scalps; fewer setups |
Execution tips:
For swing trading on H4/D1, the standard RSI 14 is typically preferred. It filters noise and allows clearer interpretation of 70/30 conditions and the 50 centerline. Practical applications:
RSI is built-in on both MetaTrader platforms. Basic setup steps are similar for RSI mt4 and RSI mt5:
Operational practices:
A disciplined RSI trading strategy forex integrates RSI’s momentum insights—70/30 zones, 50-level confirmation, divergence, and swing rejection—within a robust framework of trend, structure, and risk controls. Use the RSI 14 strategy forex as a stable baseline, then adapt RSI settings forex to your timeframe and execution style. In strong trends, remember that overbought/oversold can persist; prioritize confirmation, and rely more on divergence and centerline behavior than on blind fades.
No indicator guarantees certainty.Validate your rules through historical chart review across pairs and regimes, then forward-test with reduced size or on a demo environment, enforcing risk management on every trade. By combining RSI with complementary tools such as MACD, trendlines, and support/resistance—while honoring the momentum nature of the indicator—you can build a consistent process that captures momentum shifts without overreacting to every extreme.